 The month of October was warmer than usual in most of Europe, has just announced the Portuguese Institute of the Sea and Atmosphere (IPMA).
The month of October was warmer than usual in most of Europe, has just announced the Portuguese Institute of the Sea and Atmosphere (IPMA).
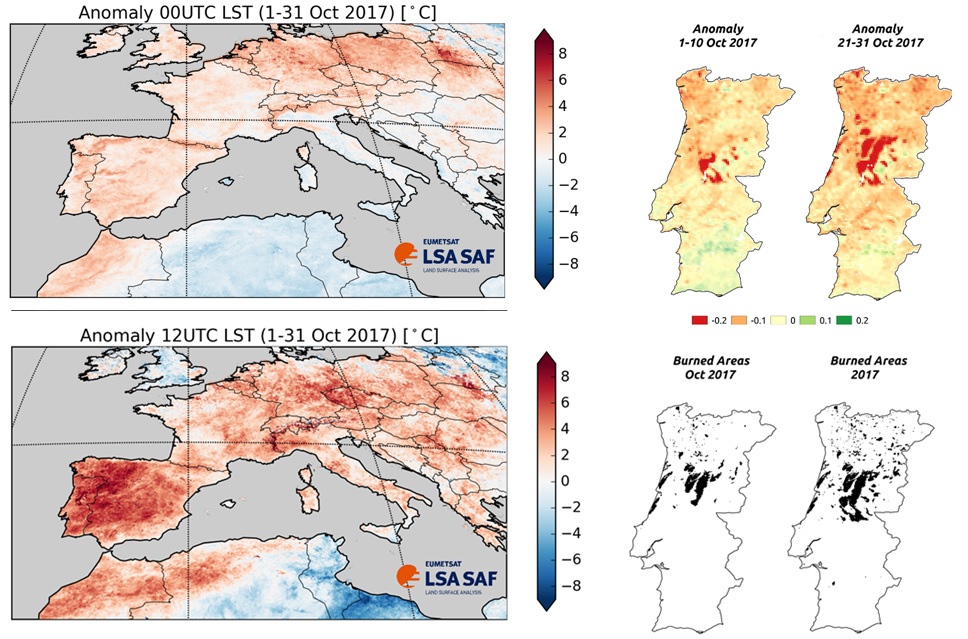
Using satellite soil surface temperature measurements Land Surface Temperature – LST), “it was found that the anomaly is particularly pronounced when the LST is maximum”, ie “during the day”.
IPMA adds that the Iberian Peninsula "shows a remarkable pattern of maximum temperature, with several regions in the north-west of the peninsula where the LST presents anomalies above 7°C".
Overnight, there were also "anomalous but not so high LST values". Areas with LST values greater than the mean values are shown in red in the image above.
The Vegetal Coverage Fraction Observed by Satellite Fraction of Vegetation Cover, FVC) on Portugal shows, according to IPMA, «the thermal stress to which the vegetation has been subjected, with values lower than the average values observed in October in the region».
However, “a large area with high FVC anomalies (< -0,2) is evident in the first 10 days of October, which corresponds to the burnt areas of the previous months, while in the last 10 days the destruction of vegetation due to October 15 fires becomes notorious». (see burned areas in the lower right panel of the image published above).
IPMA explains that "these results correspond to the maps of burnt areas provided by the Institute for the Conservation of Nature and Forests (ICNF)". Areas with less vegetation than usual are represented in red in the image above.
That institute also adds that the temperature of the soil surface is estimated from the radiances in the thermal infrared band, measured by the SEVIRI sensor on board the Meteosat Second Generation every 15 minutes under clear skies.
The LST does not correspond to the usual air temperature measurements made at meteorological stations, and there may be differences between the two temperatures of several °C.
A Satellite Application Facility on Land Surface Analysis, an IPMA-led consortium that is an integral part of the EUMETSAT ground segment (European Organization for Meteorological Satellites), provides its users with estimates of the LST every 15 minutes since 2004.

















Comments